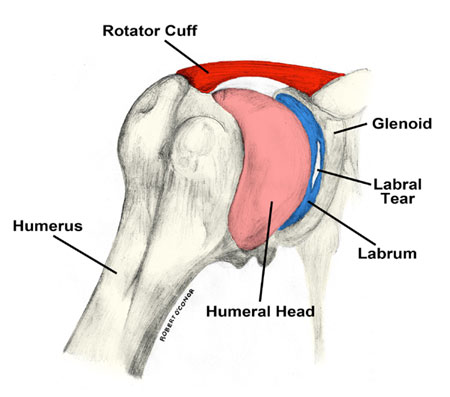
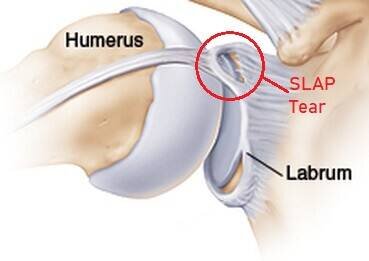
The Labrum
The labrum is a cup-like structure in the shoulder that reinforces the socket portion of the ball-and-socket joint. The joint in the shoulder is rather shallow. This causes it to rely on the labrum as well as the surrounding rotator cuff muscles. It is composed of fibrocartilage which doesn’t easily regenerate on its own.. Damage to the labrum occurs from repetitive stress to the area. An injury to the bicep which attaches to this part of the shoulder, as well as dislocations to the shoulder joint can cause damage as well.
Tears
A labral tear is most commonly seen in overhead athletes. These are athletes such as volleyball or baseball players, or to those who have repetitive dislocations of the shoulder. A SLAP tear happens when you tear the upper part of your labrum from forward to back. This high energy, quick movement can cause this to happen as it puts unwarranted stress on your bicep and labrum. A Bankart tear happens when there are recurrent dislocations of the shoulder joint. This can tear the lower portion of your labrum. This causes shoulder instability over time, which causes the shoulder to dislocate multiple times.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a labral issue include shoulder instability and weakness. You may also experience pain in the shoulder joint. Other symptoms can include grinding, clicking, or catching when you move your shoulder. Depending on the severity of the injury, you may need surgery to help correct it. As mentioned before, there is little to no regeneration of this part on its own. However, physical therapy and cortisone injections will help restore the mobility and strength. If physical therapy fails or if the initial injury is severe enough, surgery may be warranted to correct the torn labrum. This surgery can include arthroscopic cleaning of the joint, removing the torn areas, and/or relocating the bicep to prevent further stress to the area. The surgeon will determine that based on the patient situation and injury severity.
Treatment
Physical therapy is an integral part of rehabilitation of a labrum injury. This is true whether surgery is needed or not. If you have had a sports related injury, multiple shoulder dislocations or any of the symptoms above, please do not hesitate to contact our office for further evaluation.
Written by: Casey Badder PT