What is Plantar Fasciitis?
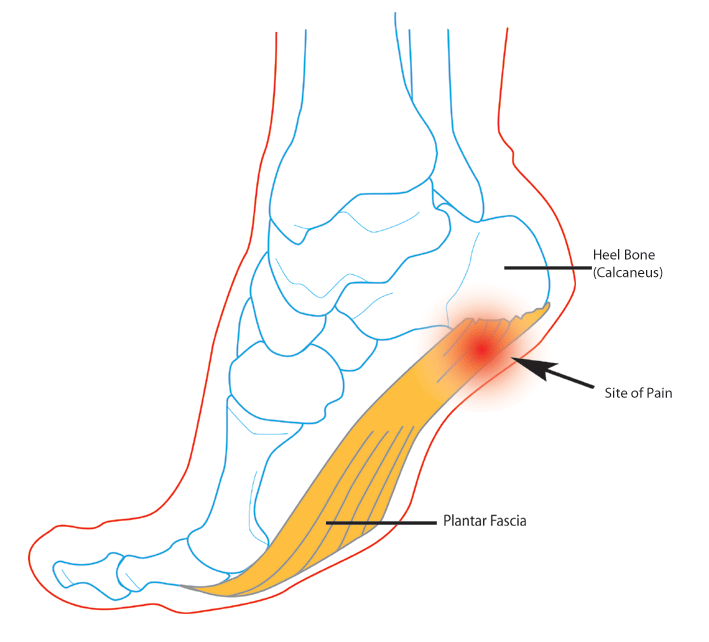
Plantar fasciitis is a condition that affects the bottom or sole of the foot. The plantar fascia consists of several broad bands of thick, tough tissue, which start at the bottom of the heel bone (called the calcaneous). Some of the bands attach to the underside of the bones of the forefoot. The others attach to the bottom of the foot at the ball of the foot (called the metatarsal heads). Because these bands are very close together, they are generally called the plantar fascia.
The plantar fascia provides a structural reinforcement for the foot and helps maintain the arch of the foot. Plantar fasciitis is a condition that happens when the plantar fascia becomes irritated and inflamed. This inflammation can have many causes such as overuse (too much running, walking or standing) or trauma (stepping on a stone, falling on the heel, etc.). Another cause may be a heel spur, which is a bony spur on the bottom of the heel usually located where the plantar fascia attaches. In some rare cases, inflammatory disease may be the cause.
Symptoms
The main symptom is pain located on the sole of the foot. The pain may be very local, in one precise spot, or it may be generalized. Most often, it seems to be at the base of the heel bone or middle of the arch. The problem may be in one or both feet. Pain usually is present or worsens with weight-bearing activities such as walking or standing.
Treatment
Treatment can take many forms. One of the first interventions is to insert a heel-pad support in the shoes to take some of the pressure off the attachment of the plantar fascia. If the pain is near the metatarsal heads, there are also shoe-insert pads for this area. Heat can help to relieve the discomfort. Ultrasound can help reduce the inflammation.
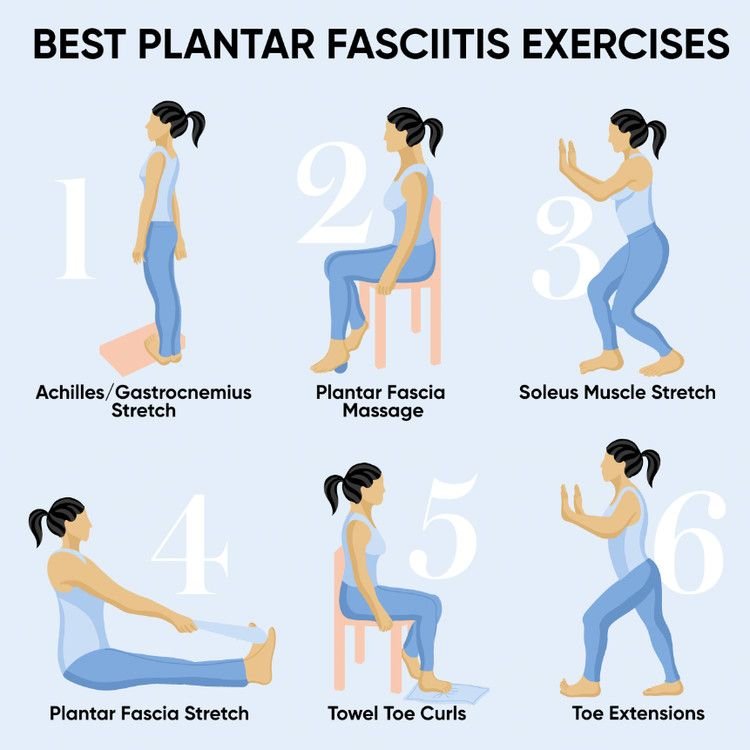
Additionally, there are specific stretches and therapeutic exercises that can be performed to help improve the condition. As the symptoms resolve, rehabilitation generally progresses into more functional-activity exercises, such as walking. For more information consult your health professional.