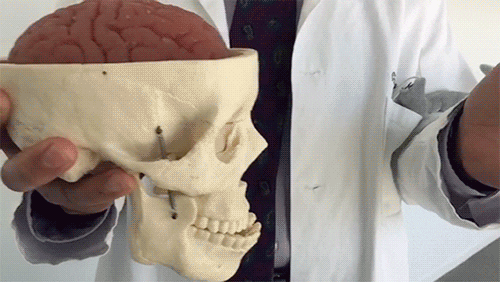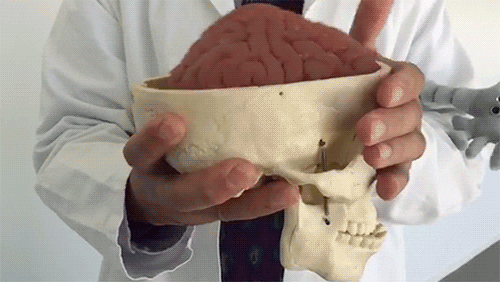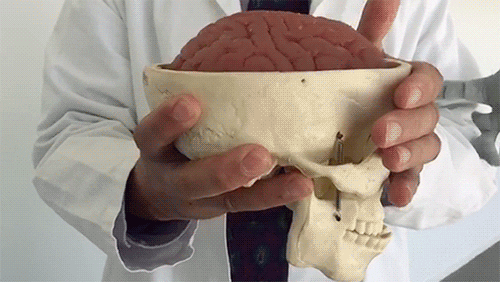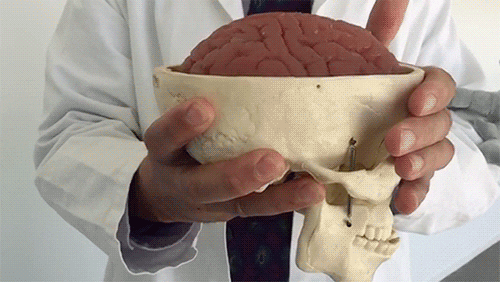
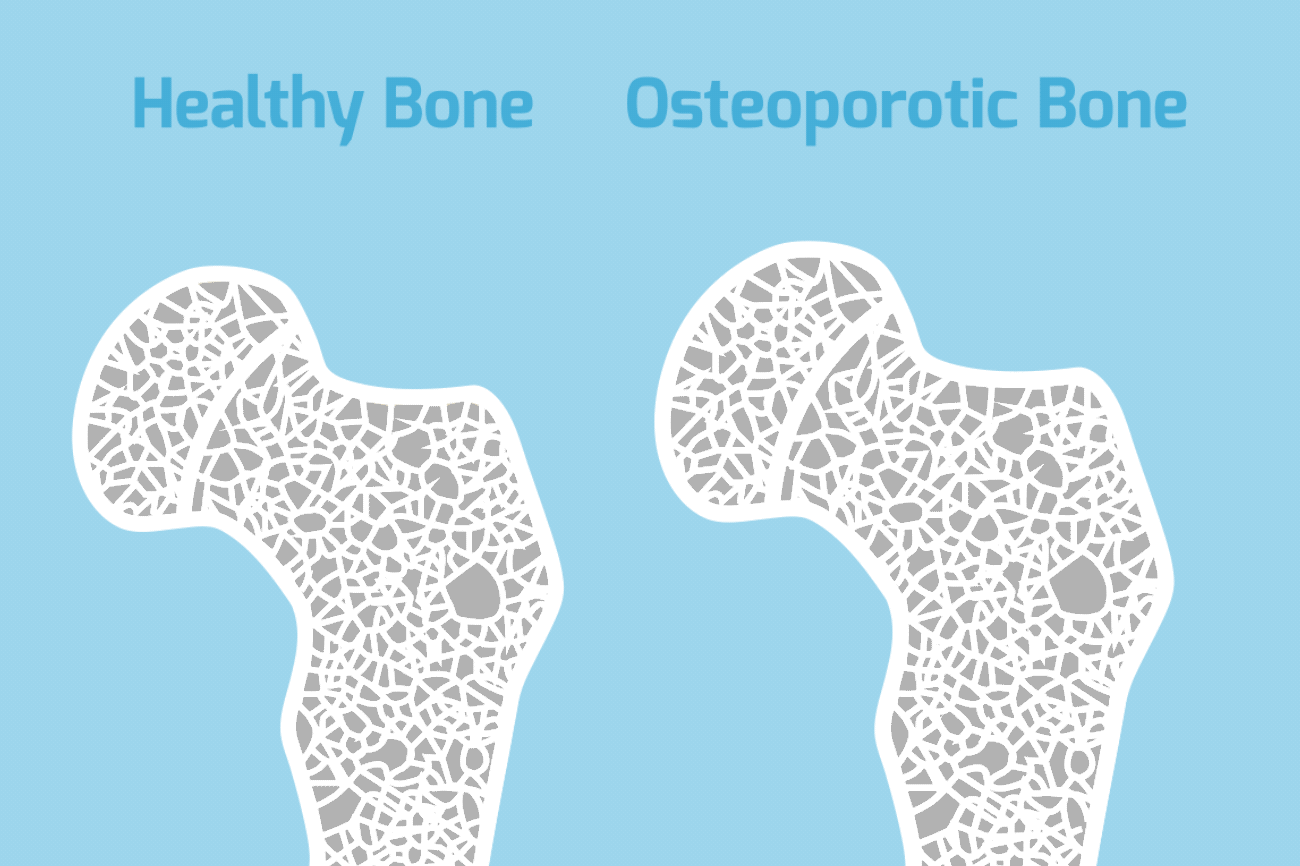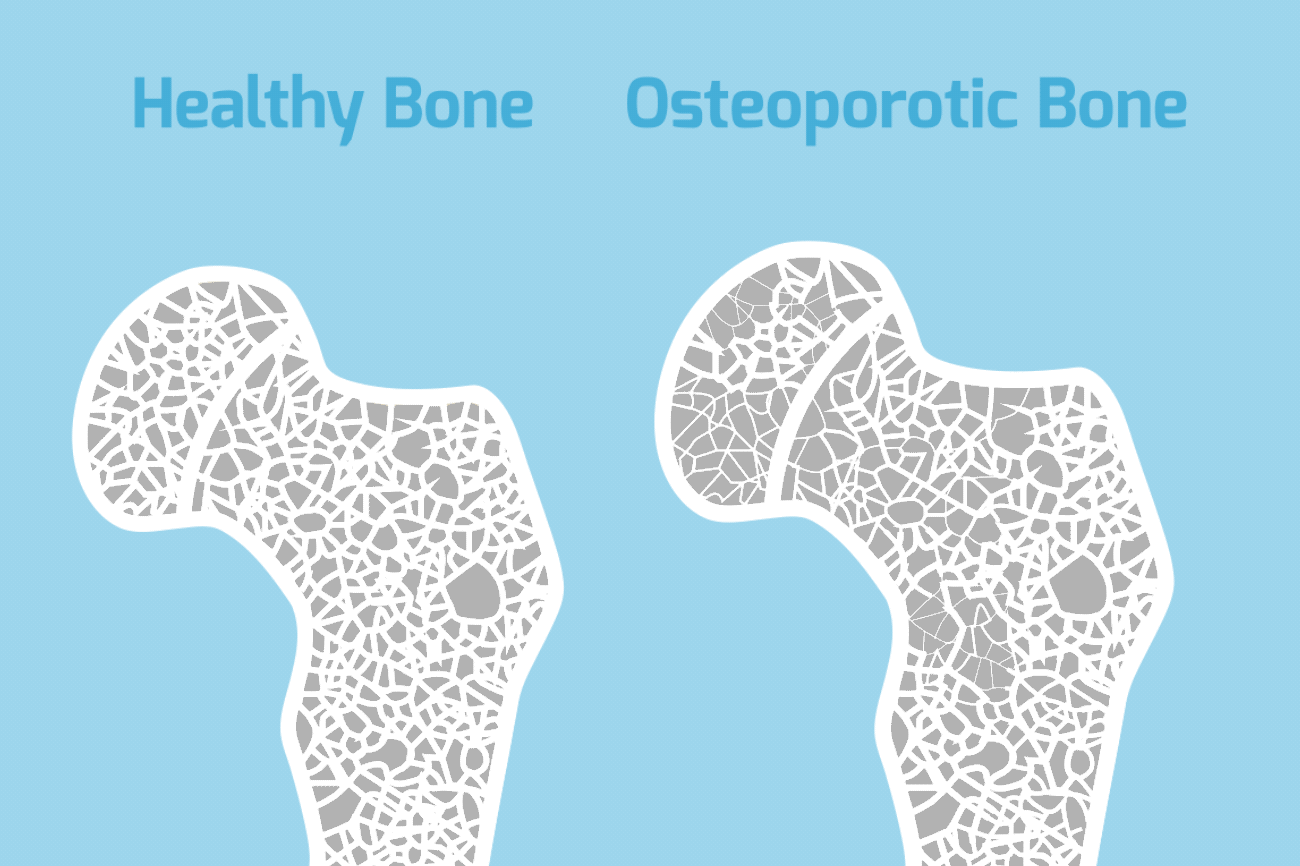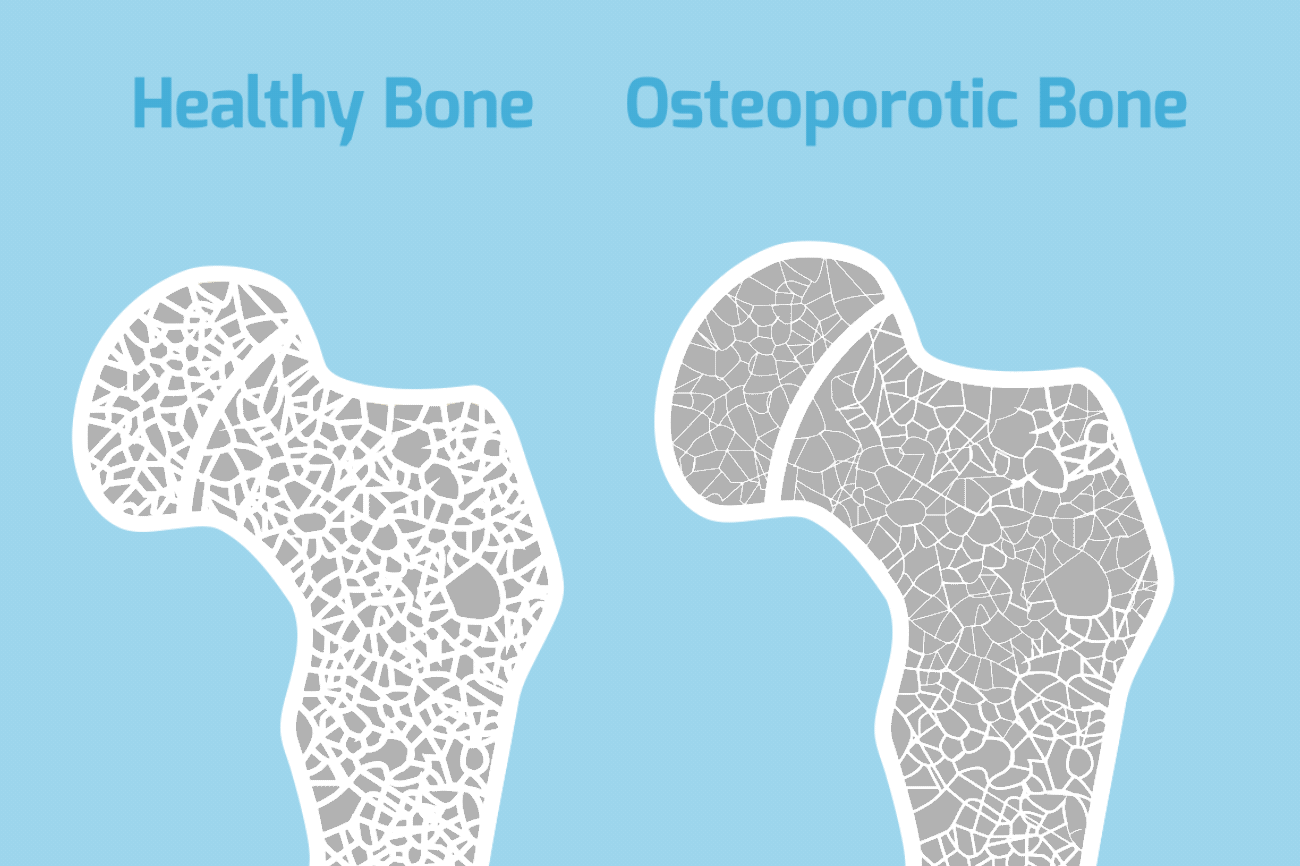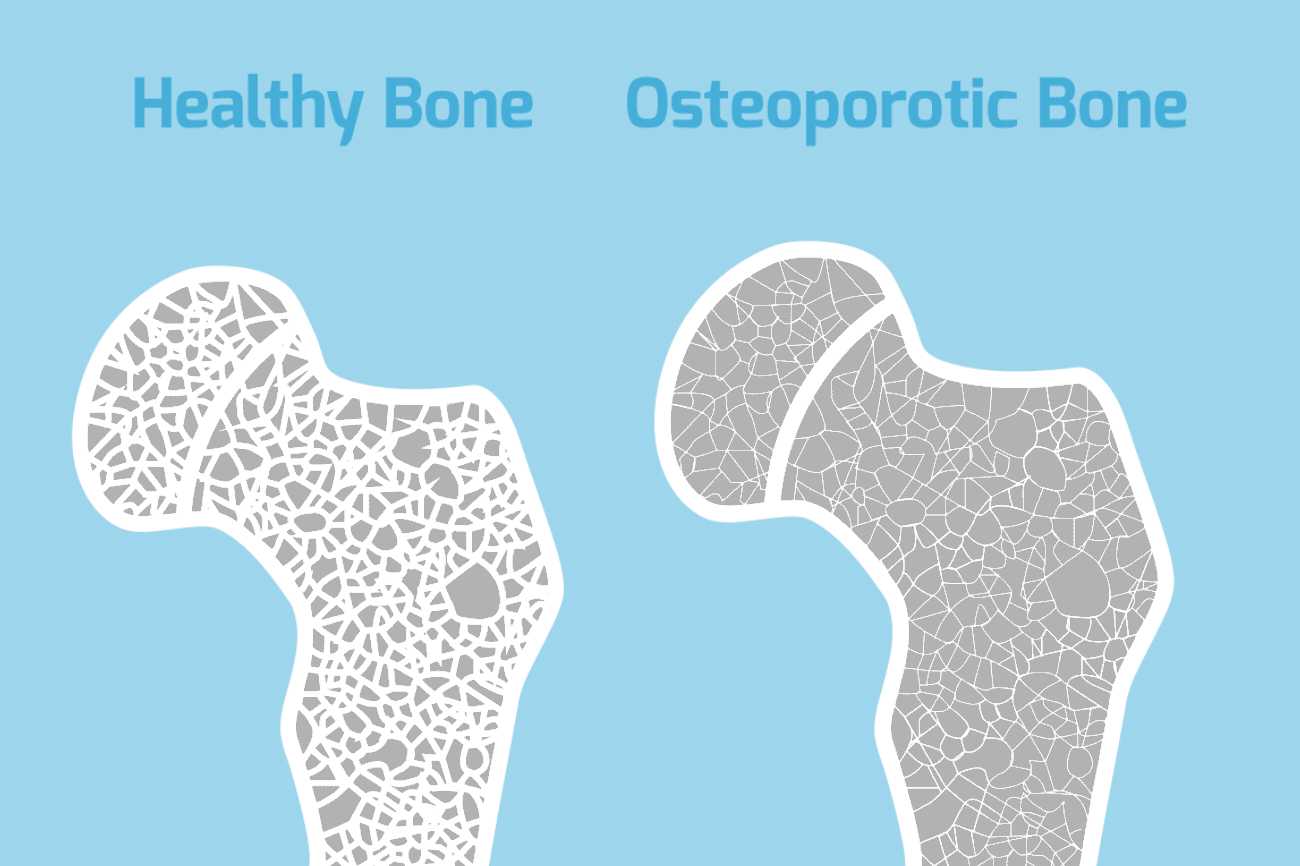
Osteoporosis is a bone disease characterized by a decrease in bone tissue. Low bone mass leads to fragile bones. It also increases your risk of fractures, especially your spine, hips, and wrists. While there is no cure for osteoporosis, it is largely preventable in most people. There are many treatment options available for those affected.
Who gets it?
This condition is most common in older women. Women who experience early menopause or have their ovaries removed before age 45 and don’t undergo hormone therapy are more likely to develop osteoporosis. Cigarette smoking, excessive alcohol, and caffeine intake contribute to the problem. So do problems with calcium absorption in the intestines. There are also some drug treatments that can induce osteoporosis.
The Silent Disease
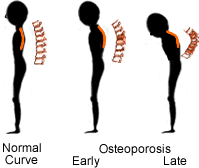
Osteoporosis is sometimes called the “silent disease”. This is because there are so few symptoms in the beginning associated with bone loss. Many people do not even know they have osteoporosis until they start getting broken bones. In severe cases of osteoporosis, symptoms include aching pain in your bones, especially in your spine. Fractures can occur without any trauma at all. The pain can be severe. But usually you don’t have the radiating pain into your arms or legs as you would with other back conditions. After repeated crush fractures in your spine, you may develop an excessive curvature in your neck or increased mid back forward bending. Hip and wrist fractures are common, especially when associated with minor falls.
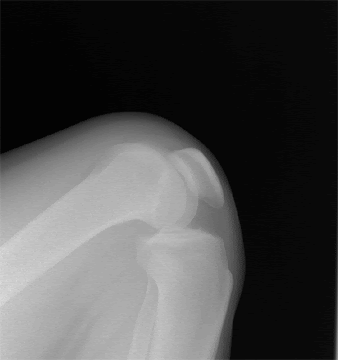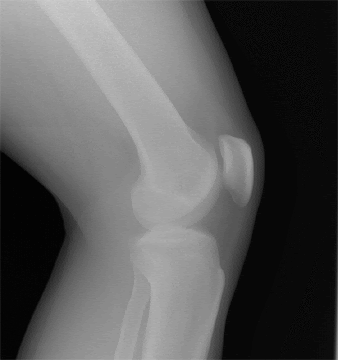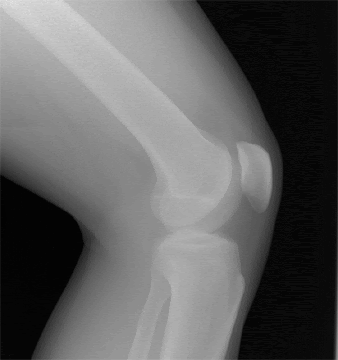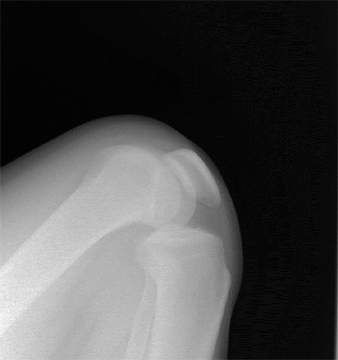
Bone density testing and X-rays are the main ways to detect osteoporosis. Your doctor can order them for you.
Treatment
Treatment of osteoporosis includes the following preventive measures:
- Exercise – Daily weight-bearing and resistance training exercise helps reduce bone loss. It also helps you maintain good muscle tone. Walking, jogging, hiking, tennis, yoga and strength training are good-weight bearing exercises.
- Nutrition – Calcium and vitamin D are needed for healthy bones. Most adults require 1000-1500 mg of calcium and 600 units of vitamin D per day. You should, however, ask your doctor to determine the right amounts for you.
- Avoid tobacco, alcohol, excessive protein, and caffeine. All of these increase your risk of developing osteoporosis. Protein is an important part of your diet and is vital for good health, but taking in high amounts of protein can cause your body to lose calcium. Caffeine in large amounts can make it hard for your body to retain calcium. Do not use tobacco. Limit your alcohol and caffeine intake.
- Medication – Hormone therapy and medications developed specifically to slow bone loss may be prescribed by your doctor.
Written by Clint Bunker PT






 (
(