Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction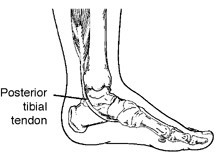
The posterior tibial tendon is one of the major supporting structures of the foot. It an important part that helps it to function while you walk. Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD) is a condition caused by changes in the tendon,that impairs its ability to support your arch. This flattens your foot. And that’s problem, because that can be painful. More painful than stepping on a Lego. 
PTTD is often called adult acquired flatfoot. That’s because it’s the most common type of flatfoot developed during adulthood. PTTD is usually progressive (which means it will keep getting worse) especially if it’s not treated early.
Causes
Weakness and overuse of the posterior tibial tendon is often the cause of PTTD. In fact, you will usually feel these symptoms after repetitive motion activities that involve your tendon, such as running, walking, hiking or climbing stairs.
Symptoms
Symptoms of PTTD may include pain, swelling, a flattening of your arch and an inward rolling of your ankle. As the condition progresses, the symptoms will change.
For example, when PTTD initially develops, you will feel pain on the inside of the foot and ankle (along the course of the tendon). The area may also be red, warm and swollen.
Later, as your arch begins to flatten, you might still have pain on the inside of your foot and ankle. But at this point, your foot and toes begin to turn outward and your ankle rolls inward.
As PTTD becomes more advanced, your arch may flatten even more. The pain often shifts to the outside of the foot, below your ankle. At this point, the tendon has deteriorated considerably, and arthritis often develops in the foot. In more severe cases, arthritis may also develop in the ankle.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Because of the progressive nature of PTTD,we advise early treatment. If treated early enough, your symptoms may resolve without the need for surgery, and progression of your condition can be stopped.
In contrast, untreated PTTD could leave you with an extremely flat foot, painful arthritis in the foot and ankle and increasing limitations on walking, running or other weight bearing activities.
Post Written By: Clint Bunker, PT